In the rapidly evolving landscape of global security, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way nations approach defense, intelligence, and strategic planning. As countries around the world invest heavily in AI technologies, the implications for national security are profound and far-reaching. This article explores the multifaceted impact of AI on national security, examining its advantages, disadvantages, challenges, and potential future developments.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global security, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way nations approach defense, intelligence, and strategic planning. As countries around the world invest heavily in AI technologies, the implications for national security are profound and far-reaching. This article explores the multifaceted impact of AI on national security, examining its advantages, disadvantages, challenges, and potential future developments.
Advantages of AI in National Security
Enhanced Intelligence Gathering and Analysis
One of the most significant advantages of AI in national security is its ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently. Intelligence agencies generate enormous quantities of information from various sources, including satellite imagery, communications intercepts, and open-source intelligence. AI-powered systems can sift through this data, identifying patterns, anomalies, and potential threats that human analysts might miss.
For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze satellite images to detect changes in military installations or unusual troop movements. Natural language processing (NLP) models can scan millions of social media posts to identify emerging security threats or track the spread of disinformation campaigns. This enhanced analytical capability allows security agencies to make more informed decisions and respond more quickly to potential threats.
Predictive Analytics and Threat Assessment
AI’s predictive capabilities offer valuable support for national security planning and strategy development. By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI models can forecast potential security risks, geopolitical developments, and emerging threats. This enables security agencies to engage in more sophisticated scenario planning, anticipating possible attacks or crises and preparing appropriate responses.
For instance, AI systems could model the potential impact of various factors – such as economic instability, climate change, or political unrest – on regional security, helping policymakers develop more effective long-term security strategies.
Cybersecurity and Network Defense
As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, AI plays a crucial role in defending critical infrastructure and sensitive networks. Machine learning algorithms can monitor network traffic in real-time, detecting anomalies and potential intrusions far more quickly and accurately than traditional security systems. AI-powered threat intelligence platforms can analyze global cyber threat data to predict and prevent future attacks.
Moreover, AI can automate many aspects of cybersecurity, such as patch management and vulnerability assessment, reducing the workload on human security teams and allowing them to focus on more complex security challenges.
Autonomous and Semi-Autonomous Systems
AI enables the development of autonomous and semi-autonomous systems that can operate in environments too dangerous or inaccessible for humans. This includes unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for reconnaissance and surveillance, autonomous underwater vehicles for naval operations, and robotic systems for explosive ordnance disposal.
These AI-powered systems can enhance military capabilities while reducing risks to human personnel. They can also operate for extended periods in harsh environments, providing persistent surveillance and intelligence gathering capabilities.
Decision Support in Crisis Situations
In times of crisis or conflict, AI can provide rapid analysis of developing situations, helping military and political leaders make informed decisions under pressure. Machine learning algorithms can process real-time data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive picture of the battlefield or crisis zone. This can lead to more effective tactical decisions and potentially reduce casualties.

Disadvantages and Risks
Vulnerability to Adversarial Attacks
While AI systems can enhance cybersecurity, they are also vulnerable to sophisticated adversarial attacks. Malicious actors can potentially manipulate the input data or exploit weaknesses in AI algorithms to deceive these systems. For example, subtle alterations to images could fool AI-powered surveillance systems, or carefully crafted text could bypass AI content filters.
This vulnerability could lead to serious security breaches or misinformation campaigns that undermine national security efforts.
Potential for Autonomous Weapons Systems
The development of fully autonomous weapons systems, often referred to as “killer robots,” raises significant ethical and security concerns. These AI-powered systems could potentially select and engage targets without meaningful human control, raising questions about accountability and the potential for unintended escalation of conflicts.
The prospect of autonomous weapons systems also creates new arms race dynamics, as nations compete to develop increasingly sophisticated AI-powered military technologies.
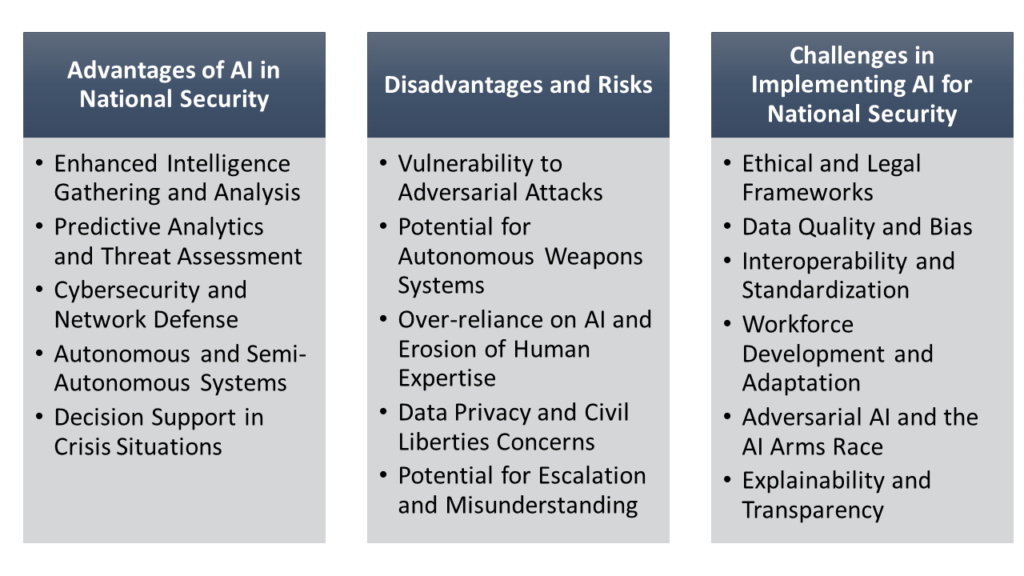
Over-reliance on AI and Erosion of Human Expertise
As AI systems become more capable, there’s a risk that security agencies may become overly reliant on these technologies, potentially eroding human expertise and judgment. Critical thinking, intuition, and the ability to understand complex geopolitical contexts are uniquely human skills that remain crucial in national security decision-making.
Over-dependence on AI could lead to a false sense of security or blind spots in threat assessment if the AI systems fail to account for novel or unprecedented scenarios.
Data Privacy and Civil Liberties Concerns
The use of AI in national security often involves processing vast amounts of data, including information about citizens. This raises significant concerns about data privacy and civil liberties. The powerful surveillance capabilities enabled by AI could potentially be misused for political control or suppression of dissent, particularly in authoritarian regimes.
Balancing national security needs with individual privacy rights will be an ongoing challenge as AI technologies become more pervasive.
Potential for Escalation and Misunderstanding
In crisis situations, the speed and automation of AI-powered systems could potentially lead to rapid escalation of conflicts. If multiple nations employ AI for military decision-making, there is a risk of creating feedback loops where AI systems react to each other’s outputs, potentially escalating tensions before human leaders can intervene.
Additionally, the “black box” nature of some AI algorithms could make it difficult to understand how they arrive at specific recommendations, potentially leading to misunderstandings or mistrust between nations.
Challenges in Implementing AI for National Security
Ethical and Legal Frameworks
The rapid advancement of AI in national security outpaces existing ethical and legal frameworks. Developing comprehensive guidelines for the responsible use of AI in defense and intelligence operations is a complex challenge. Questions arise about the appropriate level of human control over AI systems, the accountability for AI-driven decisions, and the potential consequences of AI-powered security operations on human rights and international law.
Data Quality and Bias
The effectiveness of AI systems in national security depends heavily on the quality and representativeness of the data they are trained on. Biased or incomplete data could lead to flawed analysis and potentially discriminatory outcomes. Ensuring that AI systems have access to high-quality, diverse, and unbiased data sets is a significant challenge, particularly given the sensitive nature of much national security information.
Interoperability and Standardization
As different agencies and allied nations develop their own AI systems for security purposes, ensuring interoperability between these systems becomes crucial. Establishing common standards and protocols for AI in national security applications will require extensive international collaboration and negotiation.
Workforce Development and Adaptation
Integrating AI into national security operations requires a workforce with new skill sets. Security agencies need personnel who can develop, deploy, and interpret AI systems while also understanding the broader strategic and operational contexts. Recruiting and training this new generation of security professionals presents a significant challenge.
Adversarial AI and the AI Arms Race
As nations invest in AI for national security, they must also prepare for adversaries using similar technologies. This creates a new dimension of competition, where countries race to develop more advanced AI capabilities while also working to defend against and potentially exploit weaknesses in adversaries’ AI systems.
Explainability and Transparency
Many advanced AI systems, particularly deep learning models, operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at specific conclusions or recommendations. In the context of national security, where decisions can have life-or-death consequences, the lack of explainability in AI systems poses significant challenges. Developing AI models that can provide clear explanations for their outputs while maintaining their predictive power is an ongoing area of research.
Future Prospects for AI in National Security
Quantum AI and Cryptography
As quantum computing technology matures, it could dramatically enhance the capabilities of AI in national security. Quantum-powered AI systems could break current encryption methods, necessitating the development of new quantum-resistant cryptography. Conversely, quantum AI could also enable unbreakable encryption methods, revolutionizing secure communications for intelligence and military operations.
AI-Enhanced Wargaming and Simulation
Advanced AI systems could transform military planning and training through highly sophisticated wargaming and simulation capabilities. These systems could model complex geopolitical scenarios, allowing military strategists to test various approaches and better prepare for a wide range of potential conflicts or crises.
Cognitive Electronic Warfare
AI is likely to play an increasingly important role in electronic warfare. AI-powered systems could engage in real-time spectrum analysis, rapidly identifying and countering enemy communications and radar systems. This could lead to a new era of cognitive electronic warfare, where AI systems engage in complex, dynamic electromagnetic battles.
Swarm Intelligence and Coordinated Autonomous Systems
Future military operations may involve large swarms of autonomous drones or robots coordinated by AI systems. These swarms could perform complex tasks such as reconnaissance, area denial, or even coordinated attacks, presenting new challenges and opportunities for military strategists.
AI-Driven Threat Prediction and Prevention
As AI systems become more sophisticated, they may be able to predict potential security threats with unprecedented accuracy. By analyzing vast amounts of data from diverse sources, AI could identify early warning signs of terrorist activities, cyber attacks, or geopolitical crises, allowing for more proactive security measures.
Human-AI Teaming
The future of national security is likely to involve close collaboration between human operators and AI systems. This could include AI-enhanced decision support systems for commanders, AI co-pilots for fighter jets, or AI assistants for intelligence analysts. Developing effective human-AI teaming protocols and interfaces will be a key area of focus.
AI Ethics and International Cooperation
As AI becomes more central to national security, we may see the emergence of new international bodies and agreements focused on AI governance in defense and intelligence. This could include treaties on the use of AI in warfare, similar to existing arms control agreements, as well as collaborative efforts to address global security challenges using AI.
The integration of AI into national security presents a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges. While AI offers significant advantages in terms of data analysis, predictive capabilities, and enhanced defense systems, it also raises important concerns about ethics, privacy, and the potential for unintended escalation of conflicts.
As we move forward, it will be crucial for nations to collaborate on developing ethical guidelines, regulatory frameworks, and best practices for the use of AI in national security. The goal should be to harness the power of AI to enhance security and stability while mitigating risks and preserving human rights and international law.
Balancing the potential of AI with its risks will require ongoing dialogue, adaptation, and cooperation among nations. As AI continues to evolve, so too must our approach to its use in the critical domain of national security. By addressing the challenges head-on and thoughtfully leveraging the advantages of AI, we can strive for a safer and more stable global environment.
Ahmed Banafa’s books
Covering: AI, IoT, Blockchain and Quantum Computing




